Siding cost per square foot isn’t a one-size-fits-all figure; it’s a dynamic value influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate budgeting and informed decision-making. This guide delves into the intricacies of siding costs, exploring everything from material selection and regional variations to labor expenses and hidden costs, empowering you to navigate the process with confidence.
We’ll break down the cost influences—material type (vinyl, wood, fiber cement, metal, etc.), labor rates, location, and project complexity—providing clear examples and comparisons. Learn how to estimate costs for your specific project, obtain competitive contractor quotes, and ultimately, choose the siding that best balances your budget and aesthetic preferences. We’ll also explore the installation process, potential hidden expenses, and the environmental impact of various siding materials.
Factors Influencing Siding Cost
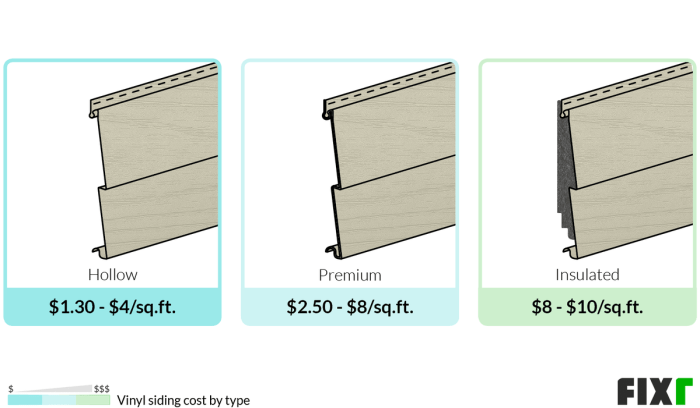
The cost of siding installation is a multifaceted issue, influenced by a variety of interconnected factors. Understanding these variables is crucial for homeowners planning a siding project, allowing for accurate budgeting and informed decision-making. This section will delve into the key elements affecting the price per square foot, enabling you to navigate the complexities of siding costs effectively.
Material Type and Cost
The choice of siding material significantly impacts the overall cost. Different materials offer varying levels of durability, aesthetics, and maintenance requirements, all of which affect the price.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Cost | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Vinyl, wood, fiber cement, metal, engineered wood | Vinyl is generally the least expensive, while metal and fiber cement tend to be more costly. Wood siding can vary widely depending on the type of wood. | Vinyl siding might cost $3-$8 per square foot, while fiber cement can range from $8-$20 per square foot. |
| Labor Costs | Wages of installers, project management, permits | Labor costs are a significant portion of the overall project expense and can vary based on location and installer experience. | Labor costs can add $3-$10 or more per square foot, depending on the complexity of the project and regional wage rates. |
| Region | Geographic location influences material and labor costs | Areas with higher costs of living generally have higher labor and material costs. | Siding installation in a high-cost-of-living area like San Francisco will be significantly more expensive than in a less populated region. |
| Project Complexity | Factors like removal of existing siding, intricate designs, or difficult access | Complex projects requiring extra time and specialized skills increase the overall cost. | A project involving the removal of asbestos-containing siding will be far more expensive than a simple installation over existing siding. |
Regional Variations in Cost
Regional differences significantly impact siding costs. These variations stem from fluctuations in material availability, labor rates, and local regulations. The following table provides a simplified comparison across three distinct regions. Note that these figures are estimates and can vary considerably based on specific project details.
| Region | Estimated Labor Cost per sq ft | Estimated Material Cost per sq ft (Vinyl) | Estimated Material Cost per sq ft (Fiber Cement) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast (e.g., New York) | $6-$12 | $4-$9 | $10-$22 |
| Midwest (e.g., Iowa) | $5-$10 | $3-$7 | $8-$18 |
| South (e.g., Georgia) | $4-$9 | $3-$6 | $7-$15 |
Cost-Effectiveness of Different Siding Materials
Comparing siding materials requires considering initial cost, lifespan, maintenance needs, and potential resale value. While vinyl offers a lower upfront cost, its shorter lifespan might necessitate replacement sooner than more expensive options like fiber cement or metal. Wood siding, while aesthetically pleasing, demands significant maintenance to prevent rot and insect damage. Metal siding offers durability but may be more expensive initially. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, considering the total cost of ownership over the material’s lifespan, is essential for making an informed decision.
Estimating Siding Costs

Accurately estimating the cost of a siding project is crucial for both homeowners and contractors. Underestimating can lead to budget overruns, while overestimating might scare away potential clients. A thorough estimation involves considering several factors, from material selection and labor costs to permits and potential waste. This section details methods for precise cost estimation and strategies for comparing contractor bids.
Methods for Estimating Siding Costs Per Square Foot
Accurate siding cost estimation requires a multi-faceted approach. Ignoring any of these aspects can lead to significant discrepancies between the estimate and the actual cost. Consider these methods for a comprehensive evaluation:
- Square Footage Calculation: Begin by accurately measuring the surface area of your home’s exterior walls that require siding. This involves calculating the length and height of each wall, subtracting areas like windows and doors, and summing the results. Remember to account for complexities like dormers and gables.
- Material Cost Estimation: Research the cost per square foot of your chosen siding material. Prices vary greatly depending on the type (vinyl, wood, fiber cement, etc.), quality, and brand. Factor in potential waste (typically 5-10% extra material is recommended). Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
- Labor Cost Estimation: Labor costs are usually quoted per square foot, and this can vary based on location, contractor experience, and project complexity. Expect higher labor costs for intricate designs or difficult-to-access areas.
- Add-on Costs: Account for additional expenses such as permits, removal of old siding (if necessary), and any necessary repairs to underlying sheathing or wall structure. These can significantly impact the overall cost.
- Using Online Calculators: Several online calculators can provide preliminary estimates based on factors such as house size, siding type, and location. While useful for initial budgeting, it’s crucial to cross-reference these estimates with professional quotes.
Calculating Total Project Cost
Once you’ve estimated the costs for materials, labor, and add-ons, calculating the total cost is straightforward. Consider this example:
Total Cost = (Material Cost per sq ft + Labor Cost per sq ft) * Total Square Footage + Permits + Waste + Other Add-ons
For instance, if material costs are $3/sq ft, labor is $2/sq ft, the house has 1000 sq ft of siding, permits cost $500, waste is 10% of material cost, and other add-ons are $200, the total cost would be: ($3 + $2) * 1000 + $500 + ($3 * 1000 * 0.1) + $200 = $6000.
Obtaining and Comparing Contractor Quotes
Getting multiple quotes is essential for ensuring competitive pricing and identifying potential issues. Contact at least three reputable siding contractors in your area. Request detailed proposals outlining materials, labor, timeline, and payment terms. Use the following template to compare their offers:
| Contractor Name | Price | Materials | Labor | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contractor A | $6000 | Vinyl Siding, Brand X | $2/sq ft | 4 weeks |
| Contractor B | $5500 | Vinyl Siding, Brand Y | $2.5/sq ft | 3 weeks |
| Contractor C | $6500 | Fiber Cement Siding | $3/sq ft | 5 weeks |
Remember to carefully review each proposal and ask clarifying questions before making a decision. Don’t solely focus on the lowest price; consider the contractor’s reputation, experience, and the quality of materials offered.
Siding Installation Process and Costs
Professional siding installation is a multi-step process requiring skilled labor and careful planning. Understanding the stages involved, along with potential unforeseen expenses, is crucial for accurate budgeting and project management. This section details the typical steps, potential hidden costs, and the process of selecting a qualified contractor.
Siding Installation Steps
The installation process typically follows a structured sequence to ensure a durable and aesthetically pleasing finish. Deviations may occur based on the type of siding and the complexity of the project, but the core steps remain consistent.
- Preparation: This critical initial phase involves thorough site preparation. It includes removing existing siding (if applicable), inspecting the underlying structure for damage, repairing any necessary issues (rotted wood, damaged sheathing), and installing house wrap or other moisture barriers. Proper preparation prevents future problems and ensures the longevity of the new siding.
- Flashing and Trim Installation: Before siding installation begins, flashing is installed around windows, doors, and other openings to prevent water penetration. Trim pieces are also installed to create a neat and finished look around these areas. This step is crucial for water management and preventing leaks.
- Siding Installation: This is the main phase of the project, where the siding panels are installed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This often involves precise measuring, cutting, and fastening of panels to ensure a straight and even appearance. The specific method will vary depending on the siding material (vinyl, wood, fiber cement, etc.).
- Caulking and Sealing: Once the siding is installed, all seams and joints are carefully caulked and sealed to prevent air and water infiltration. This step is essential for energy efficiency and preventing future damage.
- Cleanup: The final step involves a thorough cleanup of the work area, removing debris, and ensuring the site is left in a clean and safe condition. This often includes disposing of old siding materials responsibly.
Potential Hidden Costs in Siding Installation
While the initial estimate might seem comprehensive, unforeseen issues can arise during the installation process, leading to additional costs. For example, a seemingly minor issue like discovering rotted wood beneath the old siding could necessitate extensive repairs, significantly increasing the overall project expense.
- Underlying Structure Repairs: Discovering rotted wood, damaged sheathing, or insect infestation requires costly repairs before new siding can be installed. This can dramatically increase the project’s budget.
- Unexpected Material Needs: Inaccurate measurements or unforeseen complexities can lead to a need for additional materials, pushing up the overall cost. For instance, needing extra flashing or trim due to unexpected structural issues.
- Permitting Fees and Inspections: Depending on local regulations, permits and inspections may be required, adding extra costs to the project.
- Labor Cost Overruns: Unforeseen difficulties during installation can lead to increased labor costs, as the project might take longer than initially anticipated.
Selecting a Qualified Siding Contractor
Choosing a reputable and experienced contractor is crucial for a successful siding project. Thorough research and careful consideration of several factors are essential to avoid potential problems.
- Licensing and Insurance: Verify that the contractor holds the necessary licenses and insurance, including worker’s compensation and liability insurance. This protects you from potential financial liabilities in case of accidents or damages.
- References and Reviews: Check online reviews and request references from previous clients to assess the contractor’s reputation and quality of work. Look for consistent positive feedback and a history of satisfied customers.
- Detailed Contract: Ensure a detailed contract Artikels all aspects of the project, including payment schedules, materials used, timelines, and warranty information. Avoid vague or ambiguous agreements.
- Clear Communication: Choose a contractor who communicates clearly and promptly, addressing your questions and concerns effectively. Good communication is vital throughout the entire project.
Material-Specific Cost Analysis

Understanding the cost per square foot of different siding materials is crucial for accurate budgeting and informed decision-making during a home renovation or new construction project. Several factors beyond material cost influence the overall expense, including labor, permits, and waste removal. However, the material itself represents a significant portion of the total cost. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the cost, properties, lifespan, maintenance, and environmental impact of common siding materials.
The following table summarizes the cost ranges for various siding materials. It’s important to note that these are estimates and actual costs can vary depending on location, supplier, and project specifics. Labor costs are not included in these figures.
| Material | Cost Range per Square Foot | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $2 – $8 | Low maintenance, affordable, variety of colors and styles, long lifespan | Can be easily damaged, less durable than other options, may fade over time |
| Wood | $7 – $20+ | Aesthetically pleasing, natural look, can be painted or stained | High maintenance, susceptible to rot, insect damage, and warping, requires regular treatment |
| Fiber Cement | $8 – $15+ | Durable, fire-resistant, low maintenance, long lifespan, pest-resistant | More expensive than vinyl, can be brittle and prone to cracking during installation, heavier than other options |
| Metal | $10 – $25+ | Durable, long lifespan, fire-resistant, low maintenance, energy efficient | Can dent or scratch, susceptible to rust if not properly coated, high initial cost, can be noisy in rain or hail |
Vinyl Siding Properties, Lifespan, and Maintenance
Vinyl siding is a popular choice due to its affordability and low maintenance. Its properties, lifespan, and maintenance requirements significantly influence its overall cost-effectiveness.
- Properties: Made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), vinyl siding is lightweight, relatively easy to install, and comes in a wide range of colors and styles to mimic other materials like wood.
- Lifespan: With proper installation and care, vinyl siding can last 20-40 years.
- Maintenance: Requires minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning with soap and water is usually sufficient.
Wood Siding Properties, Lifespan, and Maintenance
Wood siding offers a classic and aesthetically pleasing look but demands significantly more maintenance than other options. Understanding its properties, lifespan, and maintenance needs is essential for evaluating its long-term cost.
- Properties: Available in various types of wood, each with its own properties and cost. Cedar and redwood are popular choices for their durability and natural beauty.
- Lifespan: With proper maintenance, wood siding can last 30-50 years or more, but this varies significantly depending on the wood type and climate.
- Maintenance: Requires regular cleaning, staining, or painting to protect it from rot, insect damage, and weathering. This adds to the overall cost of ownership.
Fiber Cement Siding Properties, Lifespan, and Maintenance
Fiber cement siding combines the durability of cement with the workability of wood. Its properties, lifespan, and maintenance contribute to its overall cost and value proposition.
- Properties: A composite material made from cement, cellulose fibers, and other additives. It is durable, fire-resistant, and resistant to pests and rot.
- Lifespan: Fiber cement siding typically lasts 50 years or more with minimal maintenance.
- Maintenance: Requires minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning is usually sufficient. It may need repainting every 10-15 years depending on exposure to the elements.
Metal Siding Properties, Lifespan, and Maintenance
Metal siding, often made of aluminum or steel, offers a durable and long-lasting option, but the initial investment is typically higher. Understanding its properties, lifespan, and maintenance is critical for assessing its value.
- Properties: Made from aluminum or steel, often coated with a protective layer to prevent rust and corrosion. It is durable, fire-resistant, and low maintenance.
- Lifespan: Metal siding can last 50 years or more with minimal maintenance.
- Maintenance: Requires minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning is usually sufficient. Minor dents or scratches may require repair.
Environmental Impact of Siding Materials, Siding cost per square foot
The environmental impact of siding materials should be considered alongside cost and durability. This involves examining the production process, lifespan, and disposal methods of each material.
- Vinyl: Production of PVC involves the use of fossil fuels and releases greenhouse gases. Vinyl siding is not easily recyclable and often ends up in landfills.
- Wood: The environmental impact of wood siding depends on the sourcing and processing methods. Sustainably harvested wood has a lower environmental impact than wood from unsustainable sources. Wood siding is biodegradable but may release greenhouse gases during decomposition.
- Fiber Cement: Production of fiber cement siding involves the use of cement, which has a significant carbon footprint. However, fiber cement is durable and long-lasting, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Disposal can be challenging, but some components can be recycled.
- Metal: Aluminum and steel production require significant energy, but both metals are recyclable and have a high recycling rate. Metal siding is durable and long-lasting, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Visual Examples of Siding Projects: Siding Cost Per Square Foot
Visualizing different siding projects helps homeowners understand the impact of material choice and design on both aesthetics and cost. The following examples illustrate how various siding materials and design elements contribute to the overall look and price of a project. These are representative examples, and actual costs can vary based on location, labor rates, and specific project requirements.
Small Ranch House Siding Project
This 1,200 square foot ranch house underwent a complete siding renovation using James Hardie fiber cement lap siding in a warm, earthy gray tone. The subtle texture of the fiber cement boards provided a clean, modern look, contrasting nicely with the crisp white trim around the windows and doors. The trim was also fiber cement, maintaining a cohesive aesthetic. A simple design with minimal accents kept the cost manageable. The total project cost, including materials and labor, was approximately $15,000, averaging $12.50 per square foot. The overall aesthetic is one of understated elegance, reflecting the home’s simple lines and functional design. The color choice enhances the natural surroundings, creating a harmonious blend of house and landscape.
Large Victorian Home Siding Project
A significant renovation was undertaken on a 3,000 square foot Victorian home, featuring intricate detailing and multiple gables. The homeowner chose cedar shingles in a deep, rich brown to complement the home’s historical character. The cedar’s natural variations in color and texture added depth and visual interest. To accentuate the home’s architectural features, elaborate trim work was incorporated, using matching cedar. This included intricate corner boards, decorative brackets under the eaves, and window surrounds with detailed molding. The complexity of the design and the premium material choice resulted in a higher cost, approximately $45,000, or $15 per square foot. The final result is a stunning showcase of Victorian elegance, where the siding choice perfectly complements the home’s architectural details. The deep brown of the cedar shingles gives the house a stately and sophisticated appearance.
Modern Townhouse Siding Project
This 1,500 square foot modern townhouse featured a sleek, contemporary design. The homeowner opted for a clean, minimalist aesthetic with LP SmartSide engineered wood siding in a crisp, white finish. The smooth, flat surface of the siding complemented the home’s angular lines and large windows. Minimal trim was used, focusing on clean lines and functionality rather than elaborate ornamentation. The overall project cost, including materials and labor, was approximately $18,000, or $12 per square foot. The bright white siding creates a feeling of spaciousness and modernity. The lack of extensive trim further emphasizes the clean, uncluttered design, showcasing the contemporary architectural style of the townhouse.
Design Choices and Cost Implications
Design choices, such as the type and amount of trim, the complexity of the installation, and the selection of accent pieces (like decorative shutters or stone accents), significantly impact the final cost of a siding project. Elaborate trim work, for instance, requires more labor and material, increasing the overall expense. Similarly, using premium materials like cedar or specialized metal siding will be more costly than standard vinyl or fiber cement options. Choosing simpler designs with less trim and fewer accents can help keep costs down while still achieving a visually appealing result. Careful planning and consideration of design choices are crucial for balancing aesthetics and budget in any siding project.
Successfully navigating the world of siding costs requires careful planning and informed decision-making. By understanding the key factors influencing price, employing accurate estimation methods, and selecting a qualified contractor, you can confidently undertake your siding project. Remember, comparing multiple quotes and considering the long-term costs associated with maintenance and lifespan are vital steps in ensuring a successful and cost-effective outcome. Ultimately, the right siding choice is a balance of aesthetics, budget, and long-term value.
Essential FAQs
What is the average lifespan of different siding materials?
Lifespans vary greatly. Vinyl siding can last 20-30 years, wood siding 20-50 years (depending on maintenance), fiber cement 50+ years, and metal siding 50+ years.
Do I need permits for siding installation?
Most jurisdictions require permits for exterior home renovations. Check with your local building department.
How can I find a reputable siding contractor?
Check online reviews, ask for references, verify licensing and insurance, and get multiple quotes before making a decision.
What are common hidden costs associated with siding?
Unexpected repairs to underlying sheathing, rotted wood, or additional materials needed due to unforeseen issues can significantly impact the final cost.
Can I install siding myself?
While possible for some types of siding, professional installation is generally recommended for a quality, long-lasting result and to avoid potential warranty issues.


