Siding and gutters: two seemingly simple elements that significantly impact your home’s curb appeal and structural integrity. Choosing the right siding—be it vinyl, wood, fiber cement, or metal—affects everything from maintenance needs to long-term cost. Similarly, your gutter system, whether aluminum, copper, or zinc, plays a crucial role in protecting your foundation from water damage. This guide delves into the selection, installation, maintenance, and cost considerations for both, ensuring your home’s exterior remains beautiful and protected for years to come.
We’ll explore the various types of siding and gutters available, comparing their durability, aesthetics, and cost-effectiveness. Learn how to properly maintain and repair these essential components, preventing costly damage down the line. From understanding the installation process to navigating financing options, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your home’s exterior.
Types of Siding
Choosing the right siding for your home is a crucial decision impacting aesthetics, durability, and long-term costs. This section explores the various siding materials available, comparing their properties to help you make an informed choice. We’ll delve into the pros and cons of each option, considering factors like lifespan, maintenance needs, and overall cost.
Siding Material Properties
Several materials are commonly used for house siding, each offering a unique combination of benefits and drawbacks. Vinyl, wood, fiber cement, and metal are among the most popular choices, each with distinct characteristics affecting their suitability for different climates, architectural styles, and budgets.
Vinyl Siding
Vinyl siding is a popular choice due to its affordability and low maintenance. It’s resistant to rot, insect damage, and moisture, making it a durable option in many climates. However, it can be susceptible to damage from impact and extreme temperatures, and its aesthetic versatility is somewhat limited compared to other materials. It’s often chosen for its ease of installation and wide availability in various colors. The lifespan of vinyl siding typically ranges from 20 to 40 years, depending on quality and exposure to the elements.
Wood Siding
Wood siding offers a classic, natural aesthetic that complements many architectural styles. It can be customized with various stains and finishes to enhance its appearance and longevity. However, wood siding requires significant maintenance, including regular painting or staining to prevent rot, insect infestation, and damage from moisture. It’s also more expensive than vinyl siding and is prone to warping, cracking, and fading over time. High-quality wood siding, with proper maintenance, can last 50 years or more.
Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding combines the durability of cement with the workability of wood. It’s highly resistant to fire, rot, insects, and moisture, making it a long-lasting and low-maintenance option. It also offers excellent insulation properties and can mimic the look of wood or stucco. While more expensive than vinyl, it’s generally less costly than wood and requires minimal maintenance, typically needing only occasional cleaning. Fiber cement siding can last for 50 years or more.
Metal Siding
Metal siding, often made from aluminum or steel, is exceptionally durable and resistant to fire, rot, insects, and extreme weather conditions. It’s a low-maintenance option requiring minimal upkeep. Metal siding comes in a variety of colors and finishes, but it can be prone to dents and scratches. It’s also more expensive than vinyl but less expensive than wood. Its lifespan can exceed 50 years.
Siding Material Comparison
| Material | Lifespan (Years) | Cost (Relative) | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | 20-40 | Low | Low |
| Wood | 50+ (with maintenance) | High | High |
| Fiber Cement | 50+ | Medium | Low |
| Metal | 50+ | Medium-High | Low |
Gutter Systems
Gutters and downspouts form a critical part of a home’s exterior protection system, working in concert to manage rainwater runoff and prevent costly damage. Their proper function is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the foundation and landscaping. Neglecting gutter maintenance can lead to significant problems, highlighting the importance of understanding their role and proper upkeep.
Gutter and Downspout Function in Foundation Protection
Gutters effectively collect rainwater from the roof, preventing it from flowing directly down the sides of the house. This prevents soil erosion around the foundation, which can weaken its structural support and lead to cracks or settling. Downspouts then channel this collected water away from the house’s foundation, typically directing it to a storm drain, dry well, or a designated area away from the building. This controlled drainage minimizes water accumulation near the foundation, reducing the risk of water damage, basement flooding, and foundation instability. The consistent and efficient removal of water safeguards the home’s structural integrity and longevity.
Gutter Cleaning: A Step-by-Step Guide
Safe and effective gutter cleaning is crucial for maintaining their functionality. Improper cleaning can lead to injuries or further damage. Before starting, gather necessary equipment: a sturdy ladder, work gloves, a scoop or trowel, a garden hose with a nozzle, and possibly a gutter cleaning tool.
- Inspect and Prepare: Carefully inspect the gutters for any obvious damage or blockages before climbing the ladder. Clear the area around the ladder to ensure a stable and safe working environment.
- Access the Gutters: Use a sturdy ladder, ensuring it’s placed on a level surface and firmly secured. Never overreach; move the ladder as needed.
- Remove Debris: Use a scoop or trowel to carefully remove leaves, twigs, and other debris from the gutters. A gutter cleaning tool can aid in this process, particularly for stubborn clogs.
- Flush the Gutters: Once the debris is removed, use a garden hose with a nozzle to flush out any remaining sediment or loose material. Pay attention to downspouts, ensuring they are clear and flowing freely.
- Inspect Downspouts: Check the downspouts for any blockages or damage. Clear any obstructions and ensure water flows freely to the designated drainage point.
Gutter Material Comparison
Several materials are used in gutter construction, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right material depends on factors like budget, aesthetic preferences, and climate.
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight, affordable, readily available, rust-resistant | Can dent easily, less durable than other options |
| Copper | Durable, aesthetically pleasing, long lifespan, develops a patina | Expensive, requires specialized installation |
| Zinc | Durable, long lifespan, self-healing properties | Expensive, requires specialized installation |
Gutter Sizing and Style Selection
Proper gutter size and style are crucial for efficient water management. The size should be appropriate for the roof’s surface area and the region’s typical rainfall. Larger roofs and areas with high rainfall necessitate larger gutters to handle the increased water volume. For example, a 5-inch gutter might suffice for a small house in an area with moderate rainfall, while a 6-inch or even larger gutter may be necessary for a larger house in a region with heavy rainfall. Style selection, while often a matter of aesthetic preference, should also consider the roofline and overall home design for a cohesive and visually appealing result. For instance, a traditional K-style gutter might complement a Victorian-style home, while a half-round gutter might be better suited to a more modern design.
Siding and Gutter Installation
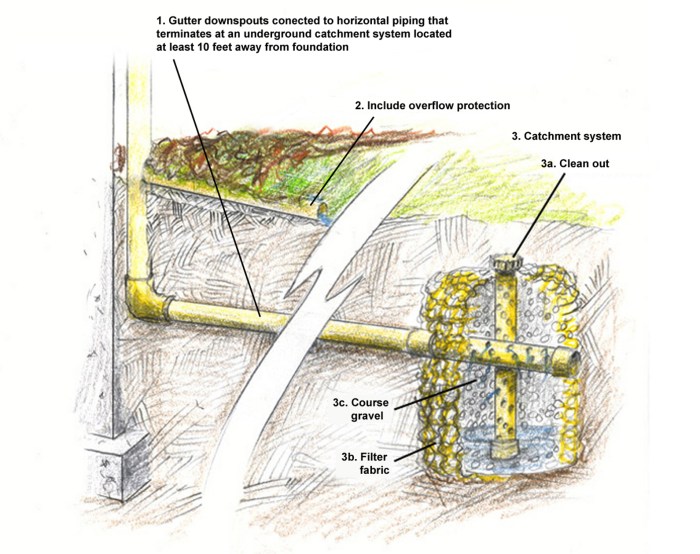
Installing siding and gutters is a significant home improvement project that enhances curb appeal and protects your home from the elements. Proper installation ensures longevity and functionality, requiring careful planning and execution. This section details the processes involved in installing vinyl siding and gutter systems, along with a checklist to guide homeowners through the preparation phase.
Vinyl Siding Installation
Vinyl siding installation involves several key steps. First, the existing siding must be removed, if applicable, and the underlying wall inspected for any damage that needs repair. Next, furring strips, if needed, are installed to create a level surface for the siding. Then, starting at a corner, the first piece of J-channel is installed, followed by the starter strip. Subsequent siding panels are then overlapped and snapped into place, working from bottom to top. Each panel should be carefully aligned and secured with nails placed near the top and bottom. Finally, the finishing J-channel is installed at the edges and around windows and doors. Throughout the process, proper measurement and cutting are crucial to ensure a neat and professional finish. Tools needed include a measuring tape, saw (circular saw or hand saw), hammer, nail gun (optional), level, and utility knife. Specific techniques, such as proper nailing to allow for expansion and contraction of the vinyl, are vital for successful installation and to avoid damage.
Gutter System Installation
Installing a gutter system involves several stages. Begin by measuring the length of the roofline to determine the amount of gutter needed. Next, install gutter hangers, spaced evenly along the fascia board, ensuring a consistent slope (typically 1/4 inch per 10 feet) for proper drainage. The gutters are then attached to the hangers, ensuring a secure and watertight fit. Downspouts are then connected to the gutters, usually at the lowest points, and secured with brackets. Elbows and extensions may be needed depending on the house design and drainage requirements. Finally, end caps are installed to complete the system. Essential tools include a measuring tape, level, drill, screws, and possibly a gutter sealant. Accurate measurements and proper slope are vital to ensure efficient water runoff and prevent water damage to the foundation.
Homeowner Checklist for Siding and Gutter Installation, Siding and gutters
Preparing for a siding and gutter installation project requires careful planning. This checklist helps homeowners organize the necessary steps:
- Obtain necessary permits.
- Secure multiple quotes from reputable contractors.
- Schedule the project during suitable weather conditions.
- Clear the area around the house of any obstructions.
- Inform neighbors about the upcoming work.
- Confirm insurance coverage and liability details.
- Ensure adequate access to electricity and water if needed.
This checklist ensures a smooth and efficient installation process, minimizing potential delays and complications.
Typical Siding and Gutter Installation Project Steps
A typical project follows a chronological sequence:
- Project planning and contractor selection.
- Permit acquisition (if required).
- Material procurement.
- Site preparation (clearing debris, protecting landscaping).
- Existing siding removal (if applicable).
- Wall inspection and repair.
- Siding installation.
- Gutter installation.
- Final inspection and cleanup.
Following these steps ensures a systematic approach, leading to a successful installation.
Maintenance and Repair

Proper maintenance and timely repairs are crucial for extending the lifespan of your siding and gutters, preventing costly damage, and maintaining your home’s curb appeal. Neglecting these essential tasks can lead to significant problems down the line, impacting both aesthetics and structural integrity. Regular inspections and proactive maintenance are key to avoiding major headaches and expenses.
Common Siding and Gutter Problems
Siding and gutters are exposed to the elements year-round, making them susceptible to a variety of issues. Common problems include leaks, cracks, damage from impact, and clogs in gutters and downspouts. Understanding these potential problems allows for prompt identification and effective solutions. Ignoring these problems can lead to water damage to the home’s foundation, structural components, and interior finishes.
Minor Siding Repair Techniques
Minor damage to siding, such as small cracks or holes, can often be repaired with readily available materials. For instance, small cracks in vinyl siding can usually be sealed with high-quality exterior-grade caulk. Larger holes might require patching with a piece of matching siding and securing it with appropriate fasteners. Always choose caulk or patching materials that are compatible with your siding type. For wood siding, wood filler and paint are often necessary to repair minor damage. Remember to always allow sufficient drying time before repainting.
Minor Gutter Repair Techniques
Minor gutter repairs often involve addressing loose or damaged sections, clogs, or leaks. Loose sections can usually be re-secured with appropriate fasteners. Small holes or leaks can often be sealed with waterproof sealant. Clogs are typically cleared using a gutter scoop or a garden hose. More extensive damage may require replacing sections of the gutter system. It’s important to ensure proper drainage to prevent water damage to your home’s foundation. Always use safety equipment such as gloves and eye protection when working on ladders.
Preventative Maintenance Tips
Regular preventative maintenance is the most effective way to prolong the life of your siding and gutters. This includes annual inspections for damage, cleaning gutters and downspouts of debris, and promptly addressing any minor issues before they escalate. For example, routinely checking for loose or damaged siding, and clearing leaves and debris from gutters after every significant storm, significantly reduces the risk of major repairs. Power washing siding (with appropriate pressure) can remove dirt and grime, enhancing its appearance and preventing build-up that could lead to damage.
Common Siding and Gutter Problems, Causes, and Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Cracked Siding | Impact, age, extreme temperature changes | Caulk (minor cracks), siding replacement (major cracks) |
| Clogged Gutters | Leaves, debris, branches | Clean gutters regularly with a scoop or garden hose |
| Leaky Gutters | Holes, loose seams, damaged downspouts | Seal holes with sealant, tighten seams, replace damaged sections |
| Sagging Gutters | Improper installation, weight of debris | Reinforce hangers, clean gutters |
| Peeling Paint on Siding | Moisture, lack of proper preparation before painting | Scrape off peeling paint, prime, and repaint |
Cost Considerations: Siding And Gutters
Understanding the financial implications of siding and gutter installation and repair is crucial for homeowners. Costs vary significantly depending on several factors, impacting both the initial investment and long-term value. This section provides a detailed breakdown of these costs, helping you make informed decisions.
Average Costs of Siding and Gutter Projects
The average cost of siding replacement ranges from $8,000 to $20,000 for a typical single-family home, while gutter installation typically costs between $1,000 and $5,000. These figures are estimates and can fluctuate drastically based on several key variables. Repair costs are naturally lower, often ranging from a few hundred dollars for minor repairs to several thousand for extensive damage. For example, replacing a single damaged section of siding might cost a few hundred dollars, while a complete gutter replacement could cost upwards of $3,000 depending on the size of the house and the materials used.
Factors Influencing Project Costs
Several factors significantly influence the overall cost of a siding and gutter project. Material selection is a major contributor; high-end materials like fiber cement or cedar siding are considerably more expensive than vinyl or aluminum. Labor costs, determined by the project’s complexity and the contractor’s rates, can also greatly impact the final price. Larger homes or projects requiring extensive repairs naturally increase costs. Geographic location plays a role too; labor and material costs vary regionally. Unexpected issues uncovered during the installation process, such as rotted wood or damaged sheathing, can lead to unforeseen expenses.
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness of Materials
While initial costs vary, the long-term cost-effectiveness of different siding and gutter materials should be considered. For instance, although fiber cement siding commands a higher upfront price, its durability and longevity translate to lower maintenance and replacement costs over the long run compared to vinyl siding which might need replacement sooner. Similarly, copper gutters, while expensive initially, are highly resistant to corrosion and can last for decades, minimizing long-term replacement costs compared to aluminum or vinyl gutters. A life-cycle cost analysis, considering initial investment, maintenance, and lifespan, should inform material selection.
Financing Options for Home Improvement Projects
Various financing options are available for home improvement projects involving siding and gutters. Home equity loans or lines of credit (HELOCs) allow homeowners to borrow against their home’s equity. Personal loans offer another avenue, though interest rates may be higher. Many contractors offer financing plans, providing flexible payment options. Finally, some manufacturers offer financing programs specifically for their products. Carefully compare interest rates, terms, and fees from various lenders before committing to a financing option. Understanding your credit score and exploring options with multiple lenders will help secure the best financing terms.
Visual Representation of Siding and Gutter Styles
Choosing the right siding and gutters can significantly enhance a home’s curb appeal and protect it from the elements. Understanding the visual characteristics of different styles is crucial for making informed decisions that complement your home’s architecture and personal aesthetic. This section explores the visual aspects of various siding and gutter options.
Clapboard Siding Appearance
Clapboard siding, also known as lap siding, is characterized by its horizontal, overlapping boards. The texture is typically smooth, though variations exist with wood grain showing through in natural wood clapboard or a textured finish mimicking wood grain in vinyl or fiber cement. Color options are virtually limitless, ranging from traditional earth tones like beige, brown, and gray to bolder hues such as deep reds, blues, and greens. The visual impact is classic and timeless, lending a clean, sophisticated look to homes, particularly those with traditional or colonial architectural styles. The overlapping boards create a subtle shadow line effect that adds depth and dimension to the façade.
Shingle Siding Appearance
Shingle siding offers a more textured and rustic appearance compared to clapboard. Individual shingles, often made of wood, asphalt, or fiber cement, are installed in overlapping rows, creating a layered effect. The texture is visibly uneven, with the shingles exhibiting a rougher surface than clapboard. Color palettes vary widely, with options ranging from natural wood tones to vibrant colors that mimic slate or cedar. The visual impact is often associated with charming, cozy, or even historic homes. The varied texture and layering of shingles create visual interest and can contribute to a home’s unique character.
Board and Batten Siding Appearance
Board and batten siding features wide vertical boards separated by narrow battens (strips of wood). This creates a strong vertical emphasis, contrasting with the horizontal lines of clapboard or shingle siding. The texture is generally smooth, although the wood grain might be visible in natural wood options. Color choices are similar to those available for other siding types, allowing for both classic and contemporary looks. The visual impact is modern and clean, often chosen for its ability to add a sleek, contemporary feel to homes. The vertical lines can make a home appear taller and more imposing.
K-Style Gutter Appearance
K-style gutters are the most common type, named for their resemblance to the letter “K” in cross-section. They are typically made of aluminum, vinyl, or steel. Aluminum gutters offer a range of colors, often mimicking the look of copper, zinc, or even painted finishes. The visual impact is unobtrusive, blending seamlessly with most home exteriors. Their clean lines and relatively flat profile make them a versatile choice for various architectural styles.
Half-Round Gutter Appearance
Half-round gutters have a more traditional and somewhat nostalgic appearance. They are typically made of copper, aluminum, or zinc, and their curved profile creates a softer, less angular look than K-style gutters. While aluminum offers a wider range of colors, copper and zinc naturally patina over time, developing unique color variations. The visual impact is charming and often complements homes with historical or rustic architectural styles. The curved shape adds a subtle elegance to the home’s exterior.
Fascia Gutter Appearance
Fascia gutters are integrated into the fascia board, the horizontal board that runs along the edge of the roof. This creates a seamless and often less visible gutter system. The material is typically the same as the fascia board—often wood, vinyl, or composite materials. Color options are determined by the fascia board material and paint choices. The visual impact is often understated, emphasizing a clean, streamlined look. They are less visually prominent than other gutter styles, allowing the architectural details of the home to take center stage.
Protecting your home’s exterior involves more than just aesthetics; it’s about safeguarding your investment. By understanding the nuances of siding and gutter selection, installation, and maintenance, you can significantly extend their lifespan and prevent costly repairs. Remember, the right choices today translate to long-term savings and peace of mind. This comprehensive guide provides the tools and knowledge necessary to make informed decisions, ensuring your home’s exterior remains both beautiful and resilient for years to come. Invest wisely in your home’s protection; it’s an investment in your future.
FAQ Summary
What is the best time of year to install siding and gutters?
Spring and fall generally offer the best weather conditions for installation, avoiding extreme heat or cold.
How often should I clean my gutters?
Ideally, clean your gutters twice a year, in spring and fall, to prevent clogs and water damage.
Can I install siding and gutters myself?
While DIY is possible for some, complex installations often require professional expertise for optimal results and warranty validity.
What are the signs of gutter damage?
Sagging gutters, leaks, rust, and pooling water near the foundation are all indicators of potential damage.
How long does siding typically last?
Lifespan varies greatly depending on material; vinyl can last 20-30 years, while fiber cement can last 50 years or more.


